When it comes time to sell commercial or residential rental property there are a few options taxpayers have to defer the gain generated. By utilizing these tactics, taxpayers have the opportunity to allow their investment to continue to grow tax-deferred. Two common strategies for tax deferral are Section 1031 exchanges and qualified opportunity zones.
Section 1031 Exchanges
A Section 1031 exchange is a trade of one investment property for another, while deferring the tax generated by the gain on sale. This exchange option is ideal when you plan to sell a rental property for more than you purchased it for. In order to defer the entire gain, there are a few qualifications that need to be met:
1. The exchange must involve like-kind property of investment or business property. Meaning both assets need to be real estate property from an investment portfolio or trade or business. The properties can be any type of real estate if it is not personal property.
2. There placement property value and loan amount must be greater or equal to the old property and loan values.
3. An intermediary must be used for the exchange to qualify for tax deferral
4. Within 45 days of selling your old property you must identify the replacement property in writing to the intermediary.
5. The purchase of the replacement property must close within 180 days of the sale of the old property.
6. You cannot receive cash back on the sale, otherwise this will result in partial recognition of gain.
If all above qualifications are met the transfer of property will be considered a successful Section 1031 exchange and be tax-free in the year of sale. The gain that was deferred will be factored into the basis of the replacement property and carried forward until that property is sold for cash. There are no limits on how many times or how frequently a 1031 exchange can be completed.
Qualified Opportunity Zones (QOZ)
Qualified opportunity zones were established to spur long-term private investment in distressed communities through the use of qualified opportunity funds (QOF). Taxpayers can choose to invest in a QOF in two ways:
1. As qualified investors – these investors elect to roll over deferred capital gains.
2. As non-qualified investors – these investors do not roll deferred capital gains. Instead, the investment is treated as an ordinary investment.
Eligible gains for purposes of the deferral are not limited to real estate. It also includes short or long-term capital gains and net Section 1231 gains.
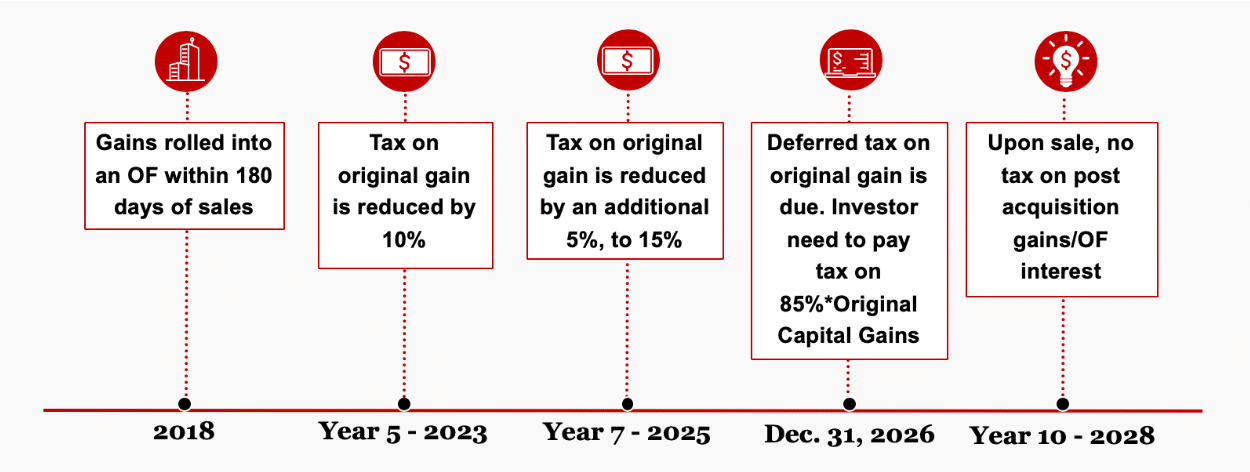
Qualified opportunity zone investments provide tiered capital gain benefits to those taxpayers that elect to roll over a deferred gain based on the following time periods:
- Five-year time frame – if investment in QOF is held for at least five years 10% of the deferred gain can be excluded from taxable income
- Seven-year time frame – if investment in QOF is held for seven years 15% of the deferred gain can be excluded from taxable income
- Investments will need to be made by 12/31/2019 in order to receive the full benefit, as the seven-year holding period ends 12/31/2026
- Tax deferral of deferred gains until end of 2026 – all deferred gains that have not been recognized by 12/31/2026 will need to be reported and recognized on the taxpayers 2026 tax return
- Ten-year time frame – if investment in QOF is held for 10 or more years, the gain on the sale of the QOF investment is 100% tax-free
Similar to section 1031 exchanges, taxpayers have 180 days from the date of the sale to invest in a QOF in order to be eligible for the gain deferral benefit. However, for gains passed to a taxpayer from a partnership or S corporation the 180-day period begins on the last day of the tax year for which the gain was received. Additionally, taxpayers only need to invest the gain, not all net proceeds in order to receive the benefit of a QOF.
Tax Deferral Timeline
Section 1031 Exchange and Qualified Opportunity Zone Comparison

If you would like more information about these tax deferral strategies or are interested in implementing one of these tactics, please contact your RDG + Partners tax advisor for assistance.